LEI involvement in the EURAD work package on Spent Fuel Characterisation
Researchers of the Lithuanian Energy Institute have been actively collaborating with colleagues from other European research organisations, technical support organisations and radioactive waste management organisations in research activities within the framework of the European Joint Programme on Radioactive Waste Management (EURAD). EURAD has been implemented as a part of the EU Research and Innovation Funding Programme Horizon 2020. One of the RD&D work packages of EURAD, WP8 “Spent Fuel Characterization and Evolution Until Disposal” (SFC), is devoted to the experimental and numerical analysis of nuclide content in spent fuel pellets and cladding materials, analysis of nuclear fuel and cladding behaviour after the discharge, as well as development, improvement and demonstration of NDA methods and systems for SNF characterisation.
The ability to determine the nuclide inventory, decay heat, gamma and neutron radiation sources of spent fuel is essential for safety and other licensing issues of the back-end of the fuel cycle such as spent fuel transportation, interim dry or wet storage and final disposal. Also, reliable prediction of spent fuel characteristics has an important influence on the overall cost of spent fuel disposal. Since majority of spent fuel characteristics are rather difficult to determine by direct measurements, numerical evaluations using purpose-developed computer codes are performed. However, accuracy of the calculation results strongly depends on nuclear data libraries, fuel assembly fabrication data (design, material compositions including impurities) and reactor operation and irradiation conditions (power, cycles, burnup, neutron spectrum). The availability of experimental measurements is extremely important for uncertainty analysis of the modelling results as well as for verification and validation of computer codes and models used for spent fuel characterisation.
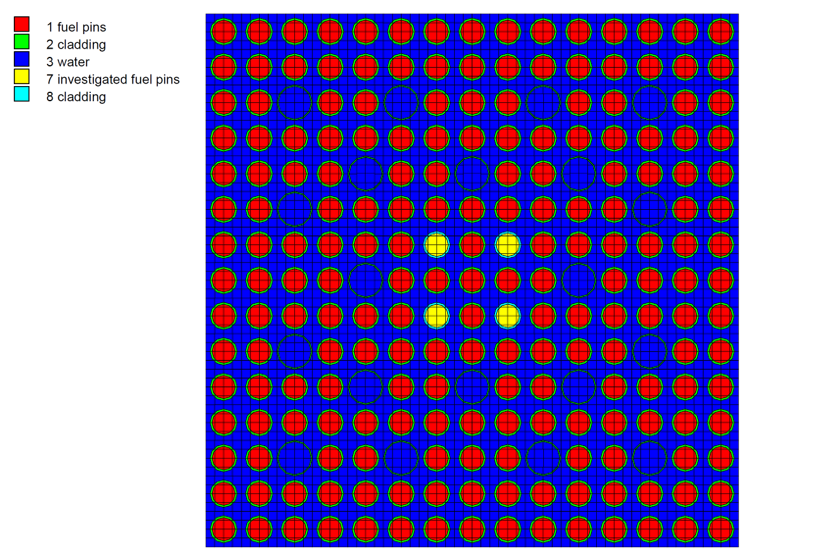
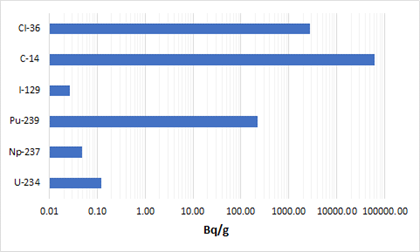
Within this work package, the LEI has contributed to Subtask 2.3 led by the Karlsruhe Institute for Technology, Institute for waste management (KIT-INE), Germany. The objective of this subtask has been to analyse inventories of activation and fission products in the Zircaloy cladding of the PWR fuel assembly with known fuel data and irradiation history. KIT-INE has performed experimental measurements of irradiated Zircaloy cladding samples at their Hot Cell facility, while the numerical modelling using stochastic and deterministic computer codes with different depletion solvers have been performed by KIT-INE (Germany), LEI (Lithuania), CIEMAT (Spain), NAGRA (Switzerland), and VTT (Finland). The measurements and calculations have shown that the presence of impurities in the Zircaloy cladding greatly affect accurate determination of the long-lived activation products, fission products and actinides (generated due to the presence of uranium impurity in the cladding material) when assessing the radiological consequences of geological disposal facilities. Under deep geological disposal conditions, the release of radionuclides from the Zircaloy cladding due to corrosion processes is faster than due to spent fuel dissolution.
Artūras Šmaižys
LEI
Arturas.Smaizys@lei.lt