New Method for Fracture Mechanics Test on the Gen IV Innovative Materials
The thin-walled tubes with small diameter are used on a large scale in nuclear power plants. More often, these tubes are used as heat exchanger tubes, steam generator tubes and nuclear cladding tubes.
These tubes are operating in severe conditions due to high temperatures and mechanical stresses combined with the effects of radiation on the material properties. The cracking behavior of thin-walled tubes is an important feature for the structural integrity during operation.
Given these considerations, to ensure the structural integrity of components which are on use in nuclear installations, it was necessary to know their resistance to the initiation and propagation of cracks. Because of their dimensions it is a quite demanding task to prepare the standard fracture mechanics specimens for classical ASTM test. All these considerations led to the need of introducing a new method for assessing the fracture material properties of tubes with thin walls. The new method is called Pin-Loading Test (PLT). The PLT-type mechanical tests are non-standard mechanical tests which are under development, and they are preferred in situations where the standardized tests are not enough accurate to study the behavior of the structural components. This type of tests was applied on the specific samples prepared from ODS steel.
Experimental work carried out by RATEN ICN Pitesti has focused on the mechanical properties characterization for the Generation IV ODS (Oxide Dispersion Strengthened) steel cladding tubes, which is an innovative material, in order to evaluate the microstructural anisotropy impact on the mechanical.
The PLT-type mechanical tests (acronym for Pin-Loading Tension test) are non-standard mechanical tests which are under development, and they are preferred in situations where the standardized tests are not enough accurate to study the behavior of the structural components. This type of test was applied on the specific samples prepared from ODS steel. The paper highlights the PLT experimental test methodology, obtaining of the geometric function necessary tool for determining KIC toughness and results processing.
Determination of the fracture mechanics parameters by the Pin-Loading Test method requires the existence of specimen with a crack (a very sharp artificial mechanical defect). In case of PLT method, tension is applied at one end of the specimen, compared to the loading in a tensile test, where the loading in applied on the whole cross-section.
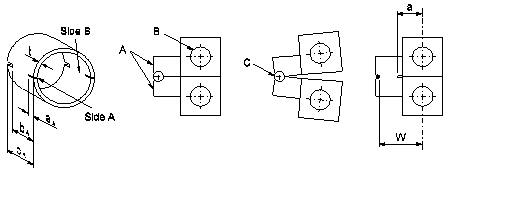
The picture shows the main characteristics of the PLT experimental arrangement. The fixture consists of two halves, which, when placed together, formed a cylindrical holder, A. The diameter of the holder allows it to be inserted into the specimen while maintaining a small gap. The fixture halves are loaded in tension through pins at position B and rotated around a pin, C, at the ends of the cylindrical holder providing similarity to the loading of a compact toughness specimen, but on two cracks. Care is taken to line up the pre-cracked notches with the intersection of the two halves of the fixture.
The advantage is that the tension required for the deformation of the specimen and the elastic deformation of the gripping system are lower than that in the uniaxial tensile test. Therefore, the elongation of the specimen is larger and the recorded data is enough to characterize the material.
Alexandru NIȚU
RATEN ICN
Alexandru.nitu@nuclear.ro